This article explains what actions and functions are available in the recipe builder's formula editor, in the AI & Analytics Engine.
What is the formula editor in AI & Analytics Engine
A formula is a group of mathematical symbols and numbers that show how to work something out. Within the Engine, the formula editor is accessible within the data wrangling feature, under the recipe builder. It provides users with the flexibility to easily prepare data using custom-made formulas.
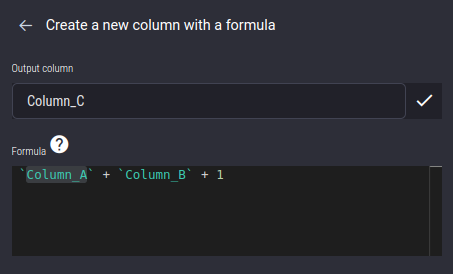 An example of the formula editor, where a new Column Column_C is created using the formula: Column_A + Column_B + 1
An example of the formula editor, where a new Column Column_C is created using the formula: Column_A + Column_B + 1
What actions use the formula editor?
There are three data-wrangling actions in the Engine that use the formula editor.
Create a new column with a formula: Creates a new column in a dataset using the user-entered formula.
Transform columns with a formula: - Transforms one or more existing columns of a dataset using the user-entered formula.
Filter rows: Filters rows of a dataset by keeping only rows that satisfy the criteria specified by the user-entered formula.
What syntax does the formula editor support?
Formulas can be constructed in the formula editor using operators and/or functions. Operands or inputs to the functions can be existing columns in the dataset or fixed values. For example, if we have two numeric columns: column_A and column_B , the following formulas can be constructed.
Using operators: Create a new column Column_C using the formula Column_A + Column_B + 1
Using functions: Create a new column Column_C using the formula LOG (Column_A)
Operators
Operators specify the type of calculation that you want to perform on elements in a formula. The operators supported currently in the Engine’s formula editor include:
Arithmetic operators: +, -, *, /, %
Comparison operators: >, >=, <, <=, ==, !=
Boolean operators: AND, OR, NOT
Functions
A function is a predefined formula that performs calculations by using specific values called arguments. The Engine currently supports 80 different functions in the formula editor for the defined actions.
|
# |
Name |
Description |
Type signatures |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
IF |
When condition (first argument) is true, evaluates the second argument. When condition is not true, evaluates the third argument. |
(Boolean, Numeric, Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
2 |
IS_NUMERIC |
Indicates whether string value is parsable to numeric |
(Text) -> Boolean |
|
3 |
IS_DATETIME |
Indicates whether string value is parsable to datetime of given strftime format |
(Text, STRING literal) -> Boolean |
|
4 |
TO_NUMERIC |
Casts string values to numeric, returns null if value is not parsable |
(Text) -> Numeric |
|
5 |
TO_DATETIME |
Casts string values to datetime taking an strftime format string as second argument. Returns null if value is not parsable. |
(Text, STRING literal) -> DateTime |
|
6 |
TO_TIMESTAMP |
Casts string values to datetime taking a Java Datetime format string as second argument. |
(Text, STRING literal) -> DateTime |
|
7 |
DAY |
The day of month as a number |
(DateTime) -> Numeric |
|
8 |
MONTH |
The month of year as a number |
(DateTime) -> Numeric |
|
9 |
YEAR |
The year as a number |
(DateTime) -> Numeric |
|
10 |
HOUR |
The hour of the day |
(DateTime) -> Numeric |
|
11 |
MINUTE |
The minute of the hour |
(DateTime) -> Numeric |
|
12 |
SECOND |
The second of the minute |
(DateTime) -> Numeric |
|
13 |
WEEKDAY |
The day of week as a number from 0 = Monday to 6 = Sunday |
(DateTime) -> Numeric |
|
14 |
WEEKOFYEAR |
The week of year as a number from 1 to 52 |
(DateTime) -> Numeric |
|
15 |
QUARTER |
The quarter in the year as a number from 1 to 4 |
(DateTime) -> Numeric |
|
16 |
DATETIME_VALUE |
Returns datetime for an ISO-format string literal |
(STRING literal) -> DateTime |
|
17 |
WEEKDAY_NAME |
Name of the day in week ("Sunday" etc.) |
(DateTime) -> Text |
|
18 |
MONTH_NAME |
Name of the month ("January" etc.) |
(DateTime) -> Text |
|
19 |
WEEKDAY_NAME_ABBREV |
Abbreviated name of the day in week ("Sun" etc.) |
(DateTime) -> Text |
|
20 |
MONTH_NAME_ABBREV |
Abbreviated name of the month ("Jan" etc.) |
(DateTime) -> Text |
|
21 |
E |
Returns the value of "e", the base of natural logarithm |
() -> Numeric |
|
22 |
PI |
Returns the value of pi |
() -> Numeric |
|
23 |
RAND |
Generates uniform random numbers between 0 and 1 |
() -> Numeric |
|
24 |
RANDN |
Generates random numbers from the standard normal distribution |
() -> Numeric |
|
25 |
ABS |
Absolute value of a number |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
26 |
ACOS |
Inverse cosine function. Computes the angle (in radians) whose cosine equals the input value. Returns null if input is out of [-1, 1] range |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
27 |
ACOSH |
Inverse hyperbolic cosine of a given input value. Returns null if input is negative. |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
28 |
ASIN |
Inverse sine function. Computes the angle (in radians) whose sine equals the input value. Returns null if input is out of [-1, 1] range |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
29 |
ASINH |
Inverse hyperbolic sine of a given value. |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
30 |
ATAN |
Arc tangent function. Computes the angle (in radians) whose tangent equals the input value. Returns null if input is out of [-1, 1] range |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
31 |
ATANH |
Inverse hyperbolic tangent of a given input value. Returns null if input is not between -1 and 1. |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
32 |
COS |
Trigonometric cosine |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
33 |
COSH |
Hyperbolic cosine |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
34 |
CEIL |
Ceiling of a number, i.e. the smallest integer not less than the input |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
35 |
DEGREES |
Computes the angle in degrees given value in radians |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
36 |
EXP |
Computes the exponential of a given value. |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
37 |
FACTORIAL |
Factorial of a given value. Fractional parts are truncated and negative input yields null. |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
38 |
FLOOR |
Floor of a number, i.e. the largest integer not greater than the input |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
39 |
INT |
Truncates a number by removing fractional parts |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
40 |
LOG10 |
Logarithm with base 10 |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
41 |
LOG |
Natural logarithm (base = Napier's constant) |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
42 |
LOG2 |
Logarithm with base 2 |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
43 |
RADIANS |
Computes the angle in radians given value in degrees. |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
44 |
ROUND |
Rounds the given input to the nearest integer. |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
45 |
SIGN |
Returns -1 for negative numbers and +1 for positive numbers |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
46 |
SIN |
Trigonometric sine |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
47 |
SINH |
Hyperbolic sine |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
48 |
SQRT |
Square root |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
49 |
TAN |
Trigonometric tangent |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
50 |
TANH |
Hyperbolic tangent |
(Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
51 |
ATAN2 |
Angle (in radians) of a line segment in two dimensions with respect to the x-axis, with origin as one end point and the given inputs as the (y, x) coordinates. Returns a value in the range [0, 2 * pi). |
(Numeric, Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
52 |
POW |
Raises the first value to the power of the second value. |
(Numeric, Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
53 |
MOD |
Computes the remainder after dividing the first value by the second value. |
(Numeric, Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
54 |
HYPOT |
Computes the hypotenuse length of a right-triangle given the lengths of its shorter sides. Equivalent to computing the magnitude of a vector in two dimensions. Together with ATAN2, this function can be used to convert two-dimensional cartesian coordinates into polar coordinates. |
(Numeric, Numeric) -> Numeric |
|
55 |
LENGTH |
Number of characters in the string |
(Text) -> Numeric |
|
56 |
LOWER |
Convert string to lower case |
(Text) -> Text |
|
57 |
UPPER |
Convert string to upper case |
(Text) -> Text |
|
58 |
INITCAP |
Change the first character in each string to upper case |
(Text) -> Text |
|
59 |
TRIM |
Remove leading and trailing whitespaces |
(Text) -> Text |
|
60 |
LTRIM |
Remove leading whitespaces |
(Text) -> Text |
|
61 |
RTRIM |
Remove trailing whitespaces |
(Text) -> Text |
|
62 |
LEFT |
First n characters of the string |
(Text, Numeric) -> Text |
|
63 |
RIGHT |
Last n characters of the string |
(Text, Numeric) -> Text |
|
64 |
SUBSTRING |
The part of the string starting at the given position to the end or up to the specified length. |
(Text, Numeric) -> Text |
|
65 |
FORMAT_NUMBER |
Format the number to a string to specified decimal places, commas separating 1000's |
(Numeric, INT literal) -> Text |
|
66 |
RLIKE |
Indicates whether column or value (first argument) matches the given regular expression (second argument). Second argument must be a string literal and not a column. |
(Text, STRING literal) -> Boolean |
|
67 |
SPLIT_DELIM |
Splits strings by a literal delimiter to produce a JSON-serialized array. The delimiter is interpreted as a literal rather than as a regular expression. The delimiter can be a maximum of 32 characters long. |
(Text, STRING literal) -> JSONArray |
|
68 |
SPLIT_PATTERN |
Splits strings by a regex pattern to produce a JSON-serialized array. The pattern is interpreted as a regex pattern rather than as a literal delimiter. The pattern can be a maximum of 256 characters long. |
(Text, STRING literal) -> JSONArray |
|
69 |
JSON_ARRAY_LENGTH |
Computes the lengths of arrays that are JSON-serialized. Null values and invalid strings in input result in -1. |
(Text) -> Numeric |
|
70 |
JSON_ARRAY_NDISTINCT |
Computes the number of unique items in arrays that are JSON-serialized. Null values and invalid strings in input result in -1. |
(Text) -> Numeric |
|
71 |
JSON_ARRAY_SORT |
Given the input JSON-serialized array, this function sorts the contents of the array and outputs it as a new JSON-serialized array |
(Text) -> JSONArray |
|
72 |
JSON_ARRAY_UNIQUE |
Given the input JSON-serialized array, this function outputs a new JSON-serialized array with the elements of the input array, but without repetitions. Output will be sorted. |
(Text) -> JSONArray |
|
73 |
JSON_ARRAY_CONTAINS |
Returns whether the input JSON array contains the specified string as one of its elements. |
(JSONArray, Text) -> Boolean |
|
74 |
JSON_ARRAY_OCCURRENCES |
Returns the number of times a specified string value occurs in a JSON array. Invalid strings and null values in input result in an output of 0. |
(JSONArray, Text) -> Numeric |
|
75 |
JSON_ARRAY_INTERSECT |
Returns the elements common to first and second arrays, removing duplicates. Result will be sorted as strings. |
(JSONArray, JSONArray) -> JSONArray |
|
76 |
JSON_ARRAY_UNION |
Returns the elements found in either the first or the second array. Duplicates will be removed and the result will be sorted as strings. |
(JSONArray, JSONArray) -> JSONArray |
|
77 |
JSON_ARRAY_CONCAT |
Concatenates the first and second arrays, order is retained and duplicates are not removed. |
(JSONArray, JSONArray) -> JSONArray |
|
78 |
JSON_OBJ_KEYS |
Gets the keys of the JSON object as a JSON array. |
(JSONObject) -> JSONArray |
|
79 |
IS NULL |
A predicate/postfix operator indicating presence of null value |
(Numeric) -> Boolean |
|
80 |
IS NOT NULL |
A predicate/postfix operator indicating absence of null value |
(Numeric) -> Boolean |
