This article explains what prediction intervals are in the Demand Forecasting Machine Learning Solution Template in the AI & Analytics Engine.
In time-series forecasting problems (such as demand forecasting), prediction intervals provide boundaries within which the actual future value is likely to fall. The boundaries defining the prediction interval vary based on the specified probability. For example: if the 90% prediction interval of a forecast is [5, 10], then there is a 90% chance that the actual future value will lie between 5 and 10. They provide a measure of model’s assessment of uncertainty around the forecasted value. A wider interval indicates higher uncertainty, while a narrower interval suggests more confidence in the forecast.
Prediction intervals give a better indication of the range of possible future values and are crucial for decision-making processes, risk management, and planning. They provide context to the forecasted value by showing how much it might vary.
The AI & Analytics Engine can generate prediction intervals for some models (e.g.: random forest). While building an app in using the demand-forecasting template, the user has the option to specify the prediction interval levels that need to be generated.
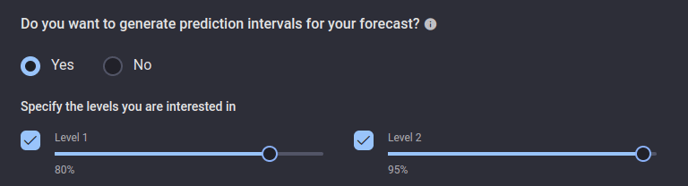
When the demand-forecasting app finishes processing, it will generate the prediction intervals for these requested levels, which can be seen in the preview as well as in the exported forecast.
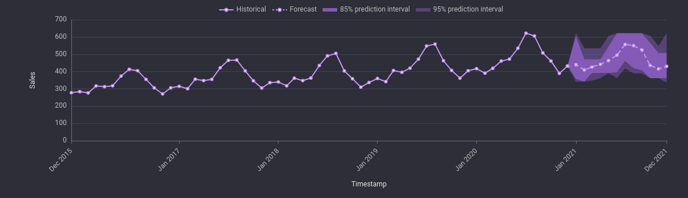
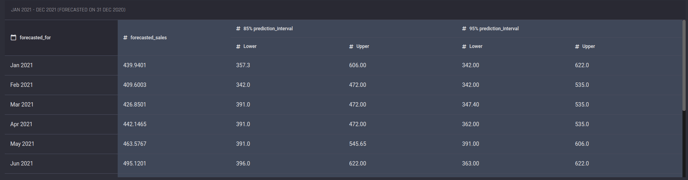
 Prediction intervals are included in the forecast result exported as a CSV
Prediction intervals are included in the forecast result exported as a CSV
💡Prediction intervals of forecasts must not be confused with confidence intervals in statistical models. For more details on how they differ, refer to this article.
